Contents
In the quest for digital excellence, businesses are constantly on the lookout for technologies that can streamline operations and provide a competitive edge. Two such transformative forces in the realm of automation are Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Artificial Intelligence (AI). While they may seem similar at a glance, their roles and capabilities in the digital ecosystem are distinct yet complementary.
What is RPA?
In the digital orchestra of modern business technology, Robotic Process Automation (RPA) plays the role of the efficiency maestro, conducting an ensemble of software bots that automate routine and monotonous tasks with remarkable precision. RPA is the unsung hero in the workplace, tirelessly performing the high-volume, repetitive tasks that humans find mundane, such as data entry, transaction processing, and even complex workflows involving multiple systems.
The Core of RPA
At its core, RPA is about rules and structured data. It operates on the principle that if a task can be defined by clear-cut rules, then it can be automated. This is not just a theoretical proposition; the practical applications of RPA are vast and varied. From automating payroll processes to streamlining bank reconciliations, RPA has proven its worth as a reliable and efficient tool for businesses looking to optimize their operations.
The Advantages of RPA
The advantages of RPA are manifold. It offers a level of speed and accuracy that is unmatched by human effort, leading to a significant reduction in processing times and errors. Moreover, RPA bots can work 24/7 without breaks, vacations, or sick days, providing a level of productivity that can transform business operations. The scalability of RPA also means that businesses can adjust their automation efforts in line with their needs, ramping up or down as required.
The Limitations of RPA
However, RPA is not a panacea for all automation challenges. Its dependency on structured data and predefined rules means that it cannot handle tasks that require judgment, intuition, or creative problem-solving. When confronted with unstructured data or unexpected scenarios, RPA bots can stumble, requiring human intervention to resolve the issues.
What is AI? The Intelligent Innovator
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the technological breakthrough that has become synonymous with the modern era’s intelligent innovation. It’s a branch of computer science that aims to create systems capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence. These tasks include learning from experiences, recognizing patterns, understanding complex data, and engaging in various forms of reasoning and decision-making.
AI systems are not programmed for specific tasks but rather designed to process data and make determinations or predictions. An AI’s learning process involves feeding large amounts of data into algorithms, allowing the system to learn from patterns or features in the data. This process is known as machine learning, and it’s one of the primary ways AI systems improve over time without human intervention.
The Complexity
The complexity of AI lies in its very nature — it’s as broad and nuanced as intelligence itself. Developing AI involves a blend of computer science, data science, mathematics, psychology, and even linguistics. The AI field encompasses several sub-disciplines, including:
- Machine Learning: The science of getting computers to act without being explicitly programmed, through learning and adaptation.
- Neural Networks: Systems modeled on the human brain that can learn from large amounts of data.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): The ability of computers to understand and process human language.
- Robotics: Machines that can interact with the physical world, often using AI to make decisions.
- Computer Vision: The ability of machines to interpret and understand visual information from the world.
Each of these areas comes with its own set of challenges and requires specialized knowledge to navigate. For instance, machine learning models need vast amounts of data to train on, and this data must be clean, well-organized, and representative of the real world. Neural networks, while powerful, can be “black boxes,” providing little insight into how they reach their conclusions, which raises ethical concerns about transparency and accountability.
Moreover, the development of AI applications must consider ethical implications, such as privacy, security, and the impact on employment. The deployment of AI must be guided by ethical principles to ensure that the technology benefits society as a whole.
In essence, AI is not just a single technology but a suite of technologies and methodologies that aim to replicate and exceed human cognitive abilities. As AI continues to evolve, it promises to unlock new frontiers in technology and society. However, navigating its complexities requires a thoughtful approach that balances innovation with responsibility.
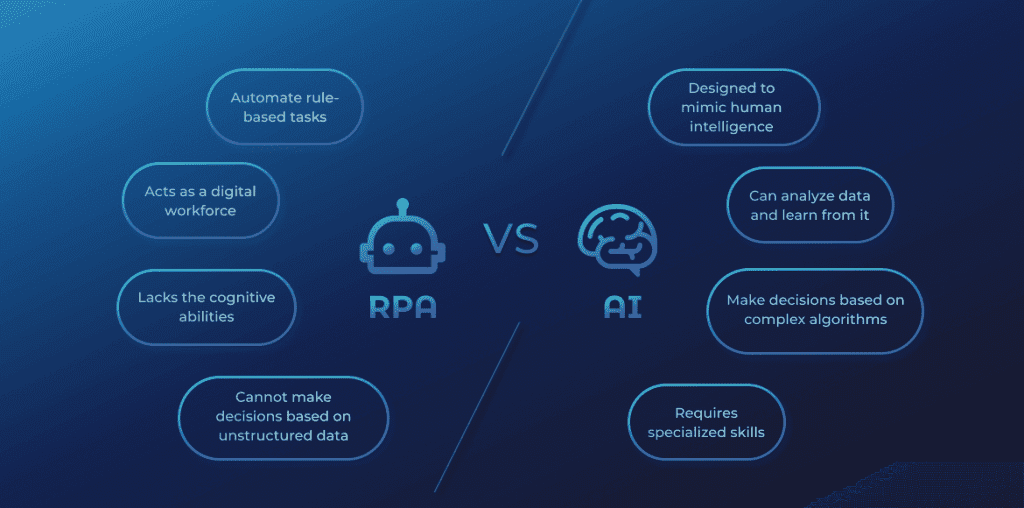


RPA and AI: Better Together
The integration of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) is ushering in a transformative era in business process automation. This fusion is not just an additive combination but a multiplicative one, where the integrated capabilities far exceed what each technology can achieve on its own. This partnership is setting the stage for a future where businesses operate with unprecedented efficiency and innovation.
Synergistic Power
The synergy between RPA and AI is a testament to the power of technological convergence. RPA provides a reliable platform for executing well-defined tasks, while AI brings the ability to interpret, predict, and make decisions. This creates Intelligent Automation (IA), a paradigm where machines don’t just perform tasks; they evolve and improve upon them. IA is redefining business operations by enabling systems that can adapt, learn from data, and make autonomous decisions, leading to significant gains in productivity and strategic insight.
RPA: The Automation Backbone
As the automation backbone, RPA offers a robust and efficient foundation for business processes. It excels in environments characterized by high-volume, repetitive tasks, providing a digital workforce that works tirelessly and without error. RPA’s role is to handle the predictable and structured tasks, freeing up human workers to focus on more complex and strategic activities. This solid foundation allows AI to be integrated more seamlessly, as it builds upon the standardized processes that RPA maintains.
AI: The Cognitive Force
AI acts as the cognitive force in this partnership, bringing intelligence and adaptability to the table. It allows for the processing of unstructured data, learning from new information, and making decisions in real-time. AI’s strength lies in its ability to not just follow a set of rules but to create new rules based on evolving data and objectives. This cognitive capability enables businesses to tackle complex problems that require an understanding of context, nuance, and the ability to adapt as situations change.
The Challenges
While the benefits are clear, integrating RPA and AI presents several challenges. The complexity of AI algorithms, the necessity for large volumes of quality data, the intricacies of integrating disparate systems, and the need for comprehensive change management strategies are among the hurdles businesses face. These challenges require a thoughtful and methodical approach to ensure that the integration of RPA and AI is successful and delivers the anticipated benefits.
Technical and Operational Complexities
The technical and operational complexities of blending RPA and AI can be daunting, requiring a strategic approach to implementation and ongoing management.
Navigating Change
The human aspect of integrating RPA and AI cannot be overlooked. Change management is crucial, as employees must adapt to new roles and processes. Organizations must invest in training and development to prepare their workforce for the changes that IA brings. This includes not only technical training but also fostering an understanding of the value that such automation brings to their roles and the business as a whole.
Conclusion: The Future of Automation
As we stand on the cusp of a new age in automation, the integration of RPA and AI offers unprecedented opportunities for businesses to optimize operations and drive innovation.


What’s Next?
If you’re intrigued by the transformative potential of RPA and AI, Scimus is here to guide you. Our team of experts can provide tailored solutions to meet your unique automation needs.