Contents
- What factors should you consider when choosing a WMS?
- How does a warehouse management system work?
- Want to develop a custom software solution?
- Types of warehouse management systems
- What are the key components of a good warehouse management system for e-commerce?
- The advantages of using an integrated eCom warehouse system
- Want to develop a custom software solution?
- What cases and challenges can you solve with warehouse integration for an e-commerce platform?
- E-commerce warehouse integrations: best practices & methods
- Introduction
- Webhooks
- Crons
- Want to develop a custom software solution?
- Best practices
- Conclusion
Warehouse Integration for e-commerce: Tips & Best Practices
As the world of business increasingly turns to e-commerce platforms, so have logistics. Global e-commerce sales aren’t expected to slow down anytime soon, and neither are the demands for efficient, cost-effective, and integrated warehousing solutions.
It is projected that the global e-commerce market will surpass $5.55 trillion in 2022. That number is expected to grow even further in a few years. These underline the importance of a warehouse management system and why companies in this space need to find ways to maximize their efficiencies while also maintaining a competitive advantage in their local market.
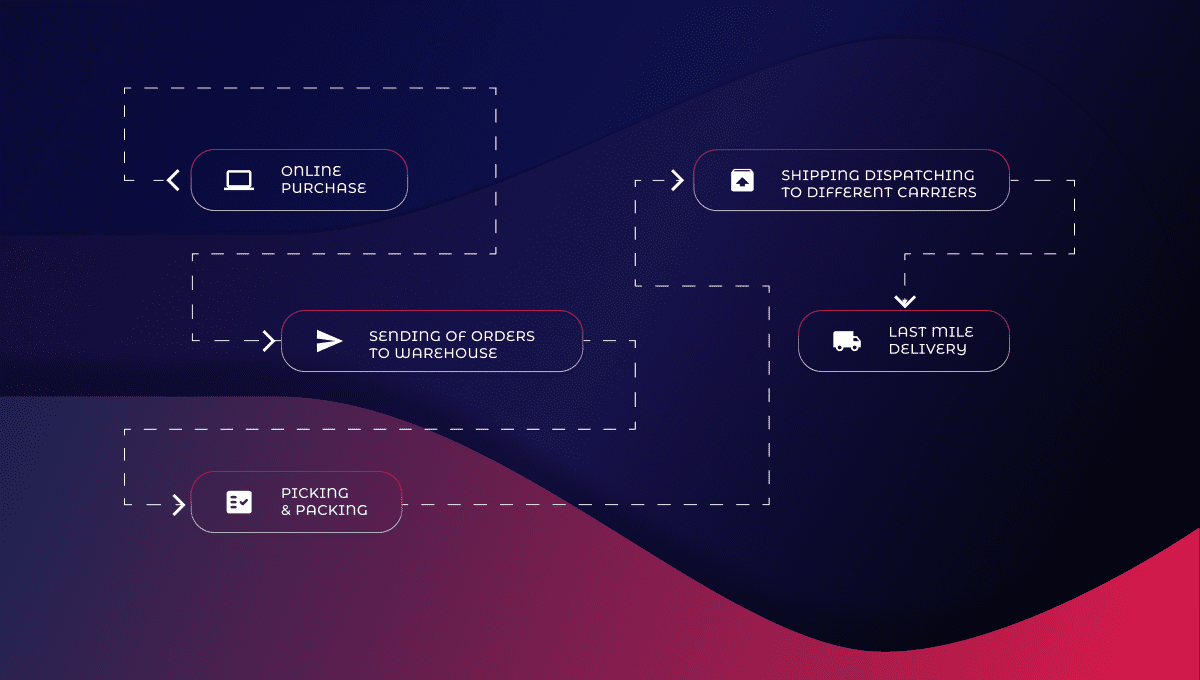
Warehouse e-commerce integration with a Warehouse Management System (WMS) can help companies achieve this goal by eliminating the need for multiple warehouses and allowing them to eliminate or reduce their facilities’ overhead costs.
Integrating your e-commerce business with an efficient WMS is a great way to make sure you’re always prepared when it comes to fulfilling orders. This article explores the definition of e-commerce warehousing software, how to find the best options for your online store, and how a seamless integration process can work well in your favor.
What factors should you consider when choosing a WMS?
First, what is a warehouse management system (WMS)?
WMS is software to manage and monitor the movement of goods from the point of origin and throughout the entire supply chain. It is an integrated system that streamlines processes such as receiving, storage, transportation, and packaging.
WMS provides you with an overview of your inventory levels, shipment locations, and demand forecasts at different delivery points. You can use this information to set up production schedules accordingly. The final objective is to make your operations more efficient and profitable by reducing waste, reusing materials, minimizing losses, and improving customer service delivery.
Choosing the most suitable warehouse management inventory system is not as easy as it sounds. There are many factors to consider when choosing the right one for your e-store.
- Customer interface & usability: The customer interface on an e-commerce platform must be intuitive so that users can quickly find what they’re looking for when browsing through products and categories. Good interfaces also include features such as product reviews, shipping options, checklists, and shopping carts that allow shoppers to purchase items easily without having to do too much research first.
- Capacity: The capacity of an e-commerce shopping cart determines how much data can be stored in it, how many products can be listed in it, and how many orders can be processed on it at once. It also has an impact on your business because it determines how fast you can process orders.
- Data integrity: This is especially an important factor when choosing the right payment gateway for your e-store. You want to make sure that all data warehouse integration is done securely and reliably between you and your users. This means that all transactions are processed correctly and there are no errors arising from mistakes or fraudsters trying to take advantage of you.
- Security: Security is a top priority for any business owner. You don’t want your customers’ information to be compromised or stolen. A good WMS platform will have a secure payment gateway and provide 24/7 support.
- Ease of use and training: A good e-commerce platform should be easy to use and require minimal training for employees who need help with the system. It should also be easy to integrate with other systems, such as point-of-sale software or marketing apps like MailChimp or HubSpot.
- Cost efficiency: A WMS should be affordable and should fit within your budget. Some of the costs may include hardware and software licenses, ongoing maintenance fees, and training.
- Scalability: You need to ensure that the WMS is scalable so that it can accommodate future growth. This means that the system has to be able to support an increase in demand over time without any issues. The scalability also needs to be easy to manage as well as flexible enough so that it can be easily adapted as per your need at any point in time.
- Support facilities and services: A good e-commerce platform will provide 24/7 customer support via phone, email, or chat. It should also have sales representatives who can answer questions about the platform itself and how it can help the growth of a small business.
How does a warehouse management system work?
A warehouse management system (WMS) is a computerized system that manages your inventory, orders, and customer information. It can also facilitate communication between employees, suppliers, and customers.
Developers use tools like Postman for API test automation to create WMS system integration technologies that help you increase efficiency by automating manual processes. The WMS connects all of your warehouse locations so that you can easily access information about your inventory, orders, and shipments from any computer.
The WMS will track each item as it moves through the supply chain — from the time it leaves your warehouse until it arrives at its destination. This means that you don’t have to keep track of every item yourself anymore!
The stages of a warehouse management system include:
- Product planning and scheduling
The first step is to define the products being shipped, the quantities being ordered, and the shipping dates. This information is then used to determine how many units will be housed in each storage area. The planning stage also includes determining the type of vehicles needed to transport the product and where these vehicles will be parked during the day.
- Inventory control
Inventory control involves keeping track of all items in stock at all times as well as knowing how much inventory remains on hand at any given time. This information is used for forecasting future demand for products and can also help managers estimate when supplies will run out if they are not replenished during regular restocking intervals.
- Warehouse layout and design
This involves designing warehouse layouts based on space requirements and employees’ productivity needs while minimizing costs associated with building materials and labor costs associated with maintaining buildings in good condition over time. In addition, this process helps managers determine whether it makes sense to relocate workers or equipment into new facilities after they have been constructed or renovated.
- Transportation and storage logistics
The next stage is to arrange for the movement of goods from suppliers, through transportation and storage, to the final destination. This includes everything from goods distribution planning in advance, to ensuring that all aspects of the transport process are completed on time.
The main purpose of the transportation process is to ensure that goods are shipped quickly, safely, and efficiently. In order to do this, you need to ensure that all the transportation stages are completed within their assigned timings.
For example, if your company ships from one e-commerce distribution warehouse to another, then you will want to make sure that your trucking vehicles have all the necessary documentation up to date as well as all the necessary permits in place before they can deliver your goods to their new destination.
- Multi-channel inventory control
The fifth stage of a warehouse management system involves monitoring inventory levels across multiple channels, including both online and offline channels. This allows warehouse for eCommerce companies to mitigate risks associated with stockouts and ensure that they are always able to meet their customers’ needs in real-time.
Want to develop a custom software solution?
Types of warehouse management systems
Generally, warehouse management systems fall into four categories:
- ERP module
ERP modules provide warehouse managers with detailed information about their inventory, supply chain, manufacturing processes, and other areas of the business. They usually contain integrated modules for sales order fulfillment, product inventory tracking, and warehousing logistics planning functions.
The ERP module is a core component of a cloud-based warehouse management system. This is where all of your company’s data is stored as well as all of your product information like SKUs, barcodes, shelving locations and more. The ERP module will provide you with reports related to inventory levels, sales trends, and more.
The main benefit of an ERP module is its integration with other business applications such as CRM systems and point of sale systems so that data can be shared across multiple systems within your organization or between your organization and suppliers or customers.
- Cloud-based WMS
Cloud-Based Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) are similar to ERP modules in that they are cloud-based. The primary difference between an ERP module and a cloud-based WMS is its deployment model. An ERP module is typically installed on-premises and accessed via a web browser; however, a cloud-based WMS can be accessed via any device with an internet connection.
Cloud-based warehouse management systems are the most popular type of system. They are usually built on an open-source platform and can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection. They typically have an integrated supply chain module (SCM), but they can also have other modules such as ERP, PIM, CRM, and more.
- Standalone system
Standalone warehouse management systems are often used for smaller companies that don’t need all the functionality of a cloud-based system. These systems can often include the same features as a cloud-based solution, but they may not offer all of the same features or integrations with other systems like ERP modules do.
- Supply chain module (SCM)
While not necessary for every organization, SCMs allow companies to manage their entire supply chain process from e-commerce warehousing and order fulfillment to shipping logistics and everything in between – all in one place. Companies can use SCMs to track their inventory levels, monitor vendor performance, and keep tabs on their vendors’ performance against their standard operating procedures.
The supply chain module is also used by companies in industries such as food and beverage, retail and manufacturing for their enterprise warehouse management. For example, a restaurant may use an SCM to track ingredients used in its dishes and ensure that it is getting the best price possible from suppliers.
What are the key components of a good warehouse management system for e-commerce?
A good warehouse management system (WMS) is essential for e-commerce companies. It can help you consolidate your inventory, reduce e-commerce storage costs and improve customer experience.
Here are some of the key components that make a good e-commerce warehouse management system:
- An integrated supply chain is one of the important warehouse management features to look out for. This means the software is easy to use and understand.
- Inventory control. It is not enough to have accurate inventory information, but it must also be easy to access and use.
- Order processing. The order processing section of the system must have everything related to the process of filling an order and sending it to the right place.
- Data entry. In this section, you can enter all the information about your products and customers into your database, including sales promotions, shipping details, etc., as well as any other relevant data that would be useful for your business operations.
- It should have an easy-to-use interface and user-friendly design.
- Compatibility with different platforms such as mobile phones, tablets, and computers so that it can be used anywhere at any time by anyone from anywhere in the world.
- Reports. The reports section displays information about your business performance in different ways, depending on what type of report you want to create. You can also set up alerts so that you will be notified when certain thresholds are reached or when certain events occur in your business environment
The advantages of using an integrated eCom warehouse system
Using an integrated eCom warehouse system means you can track inventory and sales, manage your business smarter and make informed decisions.
The advantages of using an integrated eCom warehouse system include:
Streamline inventory management system for e-commerce
An e-commerce software with inventory management can help you streamline your webshop order fulfillment process. Your inventory will be in one place, which means you will be able to manage it much more efficiently. You will not have to go through multiple steps when checking on your stock levels or updating prices, which means you can get back to doing what you do best: selling products and services!
More accurate reporting
Integrating your e-commerce and retail warehouse systems provides accurate reporting on your inventory levels, sales, and profitability. You’ll know exactly where you stand with each customer and product, so you can make better decisions about how to expand or contract your business.
Faster shipping
Shipping is one of the biggest costs in any business. That’s why having a system that makes it easy for you to quickly ship products from one location to another can help save time and money.
Reduced fraud risk
The more information that is available about who has access to your store and what they are doing there, the less likely it is that someone will try to steal from you or other customers. An integrated eCom warehouse system allows you to track all activities in real-time so you can eliminate any potential issues before they occur.
Streamline customer relationships
Another benefit of using an integrated eCom warehouse system is that it can help streamline customer relationships as well. With all your orders being handled by one system, you will be able to contact customers directly from one place instead of having multiple phone numbers and email addresses for each customer.
This means more time spent talking with each individual customer instead of wasting time trying to get in touch with them. It automates the order process and also allows you to keep track of sales leads and keep track of repeat business. This helps you know who would be a good fit for future business opportunities. It saves time and improves efficiency!
Want to develop a custom software solution?
What cases and challenges can you solve with warehouse integration for an e-commerce platform?
With the advent of e-commerce, it is inevitable that e-commerce businesses will have to face many problems and issues. These problems can be solved with e-commerce warehouse integration software.
The following are some of the issues that eCommerce WMS can solve for you:
- Data management: With the help of WMS, you can easily manage your data and find out what needs to be done with it. Moreover, you can also get a report on how much revenue has been generated by your store and what kind of products have been sold.
- Product management: In order to sell products online, you need to have them listed in your store and make them available for purchase by customers. If you are new to selling online or if your product list is not up-to-date, then this task becomes difficult for you.
However, with the help of WMS, this problem becomes easier as it helps you manage all aspects related to product listing including updating existing products in real time or adding new ones during any time period that suits you best.
- Fulfillment: If you want to ship orders from your store, then this task becomes even more difficult as there are numerous steps involved before actual shipping happens. But with an integrated WMS solution it is easy to automate all these processes and have them occur simultaneously.
- Shipping: Shipping is one of the most important parts of e-commerce because it’s the only way you can ensure your customers receive their orders on time and in good condition. With a WMS solution, shipping is much more efficient than before because all the data related to packages (i.e., weight, size) is available in real time so that your warehouse staff can easily monitor a shipment’s progress through its lifecycle.
- Order tracking: You need to know if your shipments have arrived at their destination or not! Without a WMS solution, this is something that requires a lot of manual effort from business owners who have to manually track every package that leaves their warehouse and make sure they reach their customers on time.
With an integrated WMS solution, order tracking becomes very simple as all your products are automatically tracked using GPS technology which makes monitoring shipments easy!
E-commerce warehouse integrations: best practices & methods
Introduction
After creating a number of warehouse integrations over the last couple of years, and bumping into quite a few mistakes, I have decided to share my observation and knowledge, in case someone needs to do a similar task and is looking for best practices.
So let’s review the most common setup for warehouse integrations, and the pros, and cons of each method. And then decide what we can do to combine and create quick, reliable, and repeatable integration.
Webhooks
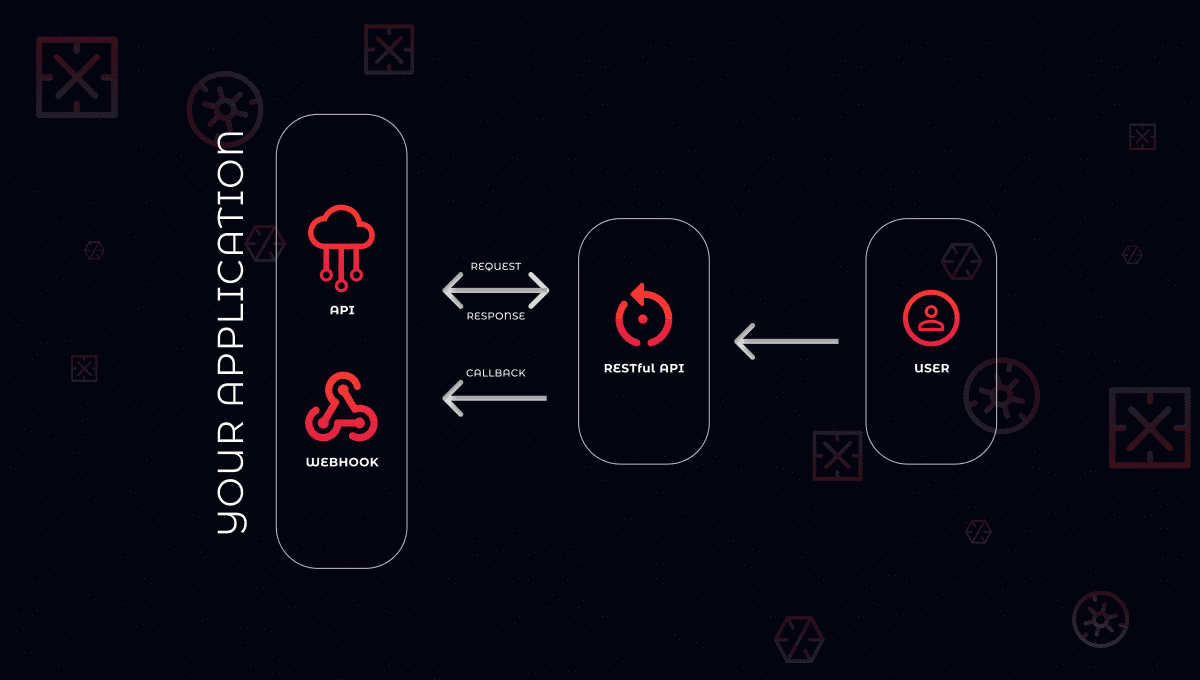
This is the most common integration flow out there. A lot of warehouses support webhooks as an integration method because it is quick and does not require a lot of resources to operate and integrate.
The main idea behind webhooks integration is that one application “notifies” another one about any change in “state”, so other applications can take certain actions based on webhook “input”.
Let’s review this example:
- We have an online store with a product, say a watch delivered by a warehouse in another state or country.
- We have a customer that makes a purchase of a watch on that online store.
- So who does webhooks integration plays here:
- An online store sends a request to the warehouse with information about the product that was purchased and usually the shipping information of the customer that purchased that product.
- Along with customer information, the online store also sends a URL, which is called a callback URL, and an action type which should serve as a trigger to call this callback URL. In our case the callback URL can be something like: /order/:id/ship and action: shipment_started.
- Warehouse packs that watch that customer purchased and send it over. This means that even shipment_started occurred and the warehouse needs to “notify” the online store about this event. So it sends a signal to the online store using the callback URL provided. This way a simple webhook integration is complete.
As we can see from the example above, webhooks are a pretty straightforward way to integrate between different applications and send “signals” from one to another without delay. But as much as any system, it has its own pros and cons which we will review right now.
Pros
Now, when we know the role webhooks play in integration with a warehouse, we can review the benefits this approach provides.
- Close to real-time execution – this means that “signal” goes from one application to another one as soon as an “event” happens.
- Simple design – when you build an integration like described above it is pretty simple and reliable as long as each party knows what to do with every event.
Cons
Does that sound too good to be true for you? Most probably you are right, there is no design ideal for each situation, so let’s review a couple of problems with webhooks.
- Reliability – webhooks integration relies on each party being online all the time, as in online store purchases can happen at any time. So in case, one party cannot accept a “signal”, this signal is lost and cannot be retrieved again automatically.
- Regression issues – if one party changes something on their side, without notifying another one(online store or warehouse in our case), intentionally(like adding a new feature and overwriting existing behavior), or unintentionally(some bug fix in one area that breaks integration) one of the applications stops to receive “signals” and a whole integration stops working.
Crons
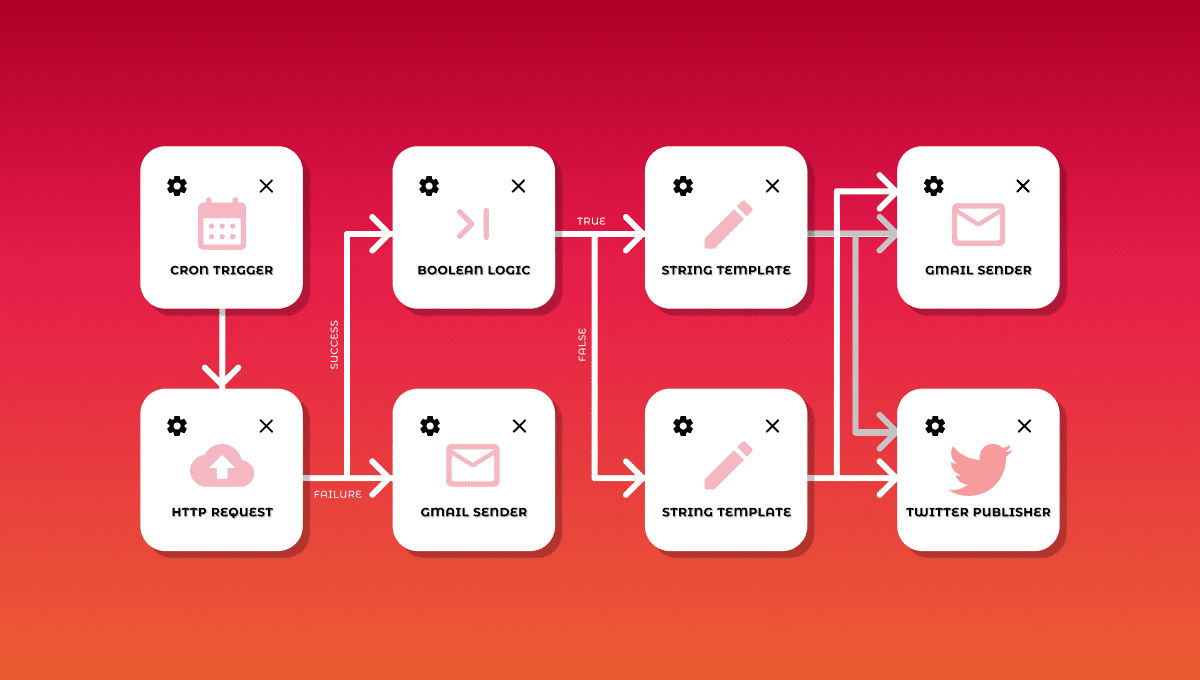
Another common integration flow is cron jobs setup for certain tasks. Some warehouse integrations do not support webhooks(especially old ones), so there is no way to “communicate” in real-time. In those cases, we have to build an integration that will be doing certain operations at a certain time.
Let’s review the same example again:
- We still have the same online store that sells the same watch delivered by a warehouse in another state or even country.
- We also have the same customer who purchases a watch on that online store.
- Now, let’s see how we can do the same integration using crons:
- The online store saves information about purchases and customer shipping information internally.
- At a certain point of time, a cron job starts and validates if there are new orders in a system that were not synced to the warehouse yet.
- When the cron job finds a new order that was not sent to the warehouse it makes a request to the warehouse with customer purchase orders and shipping information.
- The online store makes a record that the order was synced to the warehouse. We will use this information to track when order delivery starts.
- At a certain point of time, a new cron job starts that validates all synced orders and tries to understand which one was already delivered and which one is not. It just goes one by one and marks internally order delivery status.
- When delivery starts, the online store notifies a customer about delivery status and usually tracking information.
As we can see in this example, integration using crons is a bit longer, it requires more steps and a lot of looping over orders to pick one that was delivered. But this integration type has its own advantage that we will review next.
Pros
Now that we know how it works, let’s try to understand the benefits that crons provide to integration with warehouse flow.
- Reliability — crons are a very reliable method of integration because every time they are executed they will follow the same scenario. So even if the warehouse was offline an hour ago and could not accept new orders, it may be back online now and orders will be resynced again now.m
- Distinctness — every cron job is dedicated to doing one and only one thing. Either send orders to the warehouse or update the status of delivered orders. This means that a code is pretty simple to reuse or debug if needed.
Cons
Does that sound too good to be true for you? Most probably you are right, there is no design ideal for each situation, so let’s review a couple of problems with webhooks.
- Resource usage — resources used for simple operations are the biggest problem in the crons approach. Just imagine you need to match the speed of webhooks integration and all status should update close to real-time. You would need to run a cron job every minute for example and 99% of the time it will be doing nothing, but looping over orders and checking for statuses. This loads resources on an online store and warehouse just to let everyone know that nothing changes since the last time you asked. It is like a kid’s game: Are we there yet?
- Waiting time – if we want to use resources wisely we would have to wait for results to come over and set up a cron to just once an hour or even less frequently. This means that the waiting time for results will be longer than with webhooks.
Want to develop a custom software solution?
Best practices
As usual, when you are trying to do something good, you need to use the best qualities of both approaches and avoid weak spots.
So what do I suggest to do:
- Use webhooks as a main course for your integration. I suggest building an integration using regular REST API and webhooks as a base. This approach will give you flexibility, and real-time updates and will use a minimum of resources for integration.
- Add crons as a second course. In order to avoid issues with synchronization between applications, I suggest using cron jobs to resync a system in case of failure. Just add cron jobs that will be sending orders into the warehouse once a day if they were missed during a time of a purchase or sync orders that were already shipped and you will avoid 99% of issues with synchronization.
- Serve CLI command as a desert. Even if we build a super reliable system that is stable and fast, there are use cases when we need to execute crons manually, for example, if we know there is an issue with sync and we do not want to wait until midnight to get back in sync. In order to resolve this issue, I suggest adding CLI commands that will do the same tasks as cron is doing, like sync order to warehouse or update the status of a shipped order, but can be executed manually. This way we can always run a command to get a system back in sync.
Conclusion
A smooth warehouse integration and automation process by your web development services company is imperative for e-commerce environments and stores today, as a seamless flow of orders from selection to fulfillment and back again leads to happy customers and brand loyalty.
Scimus has built a dozen integrations between online stores, for all kinds of web applications, and warehouses over the last 5 years.
We had our good and bad moments, so I decided to share the knowledge collected over this time into one best practice post that can help others to avoid mistakes and use the advantages of the most common technologies out there to provide their customers a seamless experience online. As traffic is a new oil and we need to make sure that our customers feel great using applications that we build.
Getting yourself familiarized with more tips and cases like in this post can go a long way towards helping you reduce delays in shipping and getting your customers their orders quickly. These will ultimately improve your customer experience and your business profits.