Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) apps are transforming healthcare, enabling real-time patient data collection and analysis from home. But scaling these apps to handle thousands - or even hundreds of thousands - of users requires careful planning. Here’s the key to building RPM solutions that grow effortlessly:
- Choose the right architecture: Microservices allow independent scaling of features, unlike monolithic systems.
- Leverage cloud platforms: AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud offer compliance, elasticity, and cost-efficient scalability.
- Ensure data security: Implement HIPAA-compliant encryption, role-based access, and audit trails.
- Integrate IoT devices effectively: Standardize data from devices like blood pressure monitors and ensure FDA compliance.
- Streamline user experience: Design simple, intuitive interfaces for patients and efficient dashboards for clinicians.
Scaling RPM apps isn’t just about handling more users - it’s about maintaining security, integrating seamlessly with healthcare systems, and delivering a smooth user experience. With the right strategy, RPM solutions can meet growing demand while improving patient care and operational efficiency.
Demo Tour of Remote Patient Monitoring Software
Building a Scalable Architecture for RPM Apps
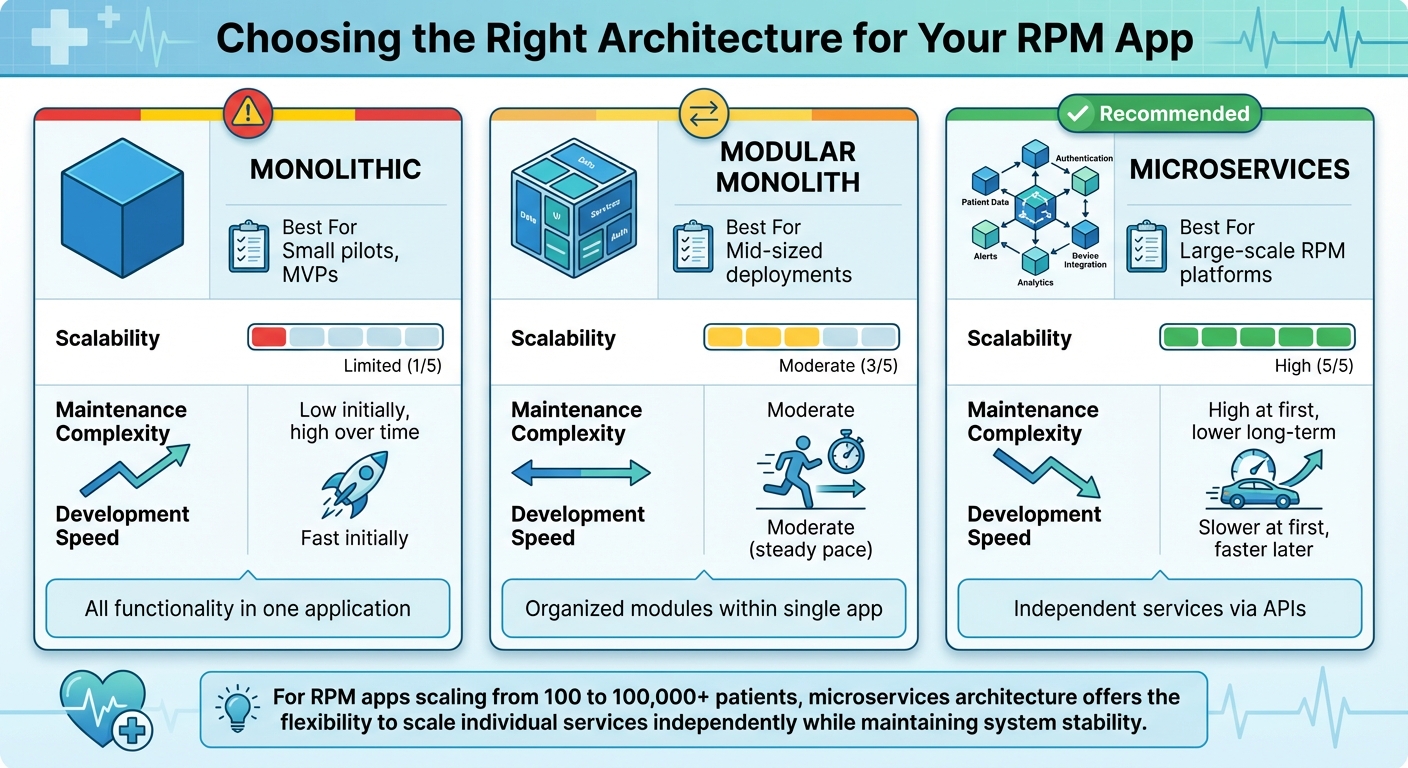
RPM App Architecture Comparison: Monolithic vs Modular vs Microservices
When it comes to scaling your Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) app from 100 to 100,000 patients, your architectural choices make all the difference. Traditional monolithic EHR systems, which bundle all features into a single codebase, often struggle with scalability and make independent updates almost impossible.
Microservices architecture has become the go-to solution for modern EHRs and RPM apps. This approach breaks your application into smaller, independent services, each focused on a specific function - like managing patient data, integrating devices, or running analytics. The beauty of this system? If there's a sudden spike in new patient enrollments, you can scale just the affected service, keeping the rest of the system stable. This modular setup allows you to scale only what’s needed, saving both time and resources.
For instance, in February 2024, the ScalableDigitalHealth framework used AWS storage and Lambda functions to process real-time IoT health data, including ECG readings, body temperature, and oxygen saturation. They employed Kubernetes with horizontal pod autoscaling, powered by custom metrics and a Prometheus adapter, to balance accessibility and cost-efficiency.
Choosing the Right Architecture: Modular, Microservices, or Monolith
Your choice of architecture influences everything from how quickly you can develop features to how smoothly your app will scale. Here’s a breakdown of the three main options:
- Monolithic architectures: These combine all functionality into one application. While this works for small-scale pilots, it quickly becomes a headache as your user base grows. Every update requires redeploying the entire system, and a bug in one feature can crash everything.
- Modular monoliths: This structure organizes code into distinct modules within a single application. It offers some benefits in organization and simplicity, but scaling individual components remains a challenge.
- Microservices: The most flexible and scalable option. Each service operates independently, communicates via APIs, and can be updated or scaled without affecting the rest of the system. For example, if your app experiences a surge in device data uploads, you can scale just the data ingestion service while leaving patient dashboards and clinician notifications untouched. Plus, if one service fails, the rest of the system keeps running.
| Architecture Type | Best For | Scalability | Maintenance Complexity | Development Speed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monolithic | Small pilots, MVPs | Limited | Low initially, high over time | Fast initially |
| Modular Monolith | Mid-sized deployments | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate |
| Microservices | Large-scale RPM platforms | High | High at first, lower long-term | Slower at first, faster later |
Using Cloud Technologies for Scalability
Cloud platforms like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud give you the tools to handle fluctuating patient loads without massive upfront costs. These platforms come with built-in compliance for standards like HIPAA, HITRUST, and GDPR, saving you the hassle of building your own compliance infrastructure.
Elastic scaling is a standout feature, automatically adjusting resources based on demand. For example, during peak times when clinicians are actively reviewing patient data, the system scales up. During quieter periods, it scales down to save costs. Features like auto-scaling groups, multi-zone failover, and load balancers ensure your app stays responsive even during traffic spikes.
Serverless computing, such as AWS Lambda, is another game-changer. It allows you to process data efficiently and integrate microservices seamlessly, all while paying only for the compute time you actually use. Event-driven architectures, powered by tools like Apache Kafka, Google Pub/Sub, or RabbitMQ, decouple services and trigger workflows based on real-time data changes. This ensures smooth communication between services and prevents bottlenecks.
When choosing a cloud provider, consider your tech stack and integration needs:
- AWS: Offers HealthLake for managing large-scale health data.
- Google Cloud: Features a Healthcare API designed for FHIR-based interoperability.
- Azure: Provides Health Data Services for unified health data management.
All three platforms support HIPAA-eligible services and offer specialized tools tailored for healthcare applications.
Designing Data Flow and Healthcare System Integration
RPM data doesn’t just appear where it’s needed - it travels through multiple layers before reaching clinicians. IoT devices send data through mobile apps to a cloud backend, where it’s processed, analyzed, and stored. From there, relevant insights are sent to EHR systems and clinician dashboards.
To ensure this flow works seamlessly, design your data pipelines to preserve integrity and match processing speeds to clinical requirements. For instance, critical alerts, like abnormal vitals, need real-time processing, while routine measurements can be batched for efficiency. The ScalableDigitalHealth framework used a Lambda event service instead of MQTT for receiving data from smartphone apps, citing its efficiency in processing, microservices integration, and strong authentication measures.
Interoperability standards like FHIR, HL7, and SMART on FHIR are essential for smooth data exchange with existing healthcare systems. FHIR, in particular, has become the preferred standard, offering RESTful APIs that simplify integration compared to older protocols like HL7 v2. By adopting FHIR, your RPM app can communicate with virtually any EHR system without requiring custom integrations for each vendor.
Message brokers also play a key role in managing data flow. They queue incoming device data, ensuring nothing gets lost during traffic spikes, and allow asynchronous processing. This event-driven approach prevents bottlenecks and ensures that different parts of your system can handle data at their own pace while maintaining overall consistency.
Next, we’ll dive into how these architectural choices lay the groundwork for data security and compliance in RPM apps.
Data Security and Compliance in RPM Apps
Once you've built a scalable architecture, the next big priority is securing patient data. Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) apps handle large volumes of sensitive information, including Protected Health Information (PHI). This means they must comply with HIPAA - a U.S. law passed in 1996 that establishes national standards for safeguarding patient health data.
Protecting this data involves implementing administrative, physical, and technical safeguards throughout your system. For example, role-based access controls ensure users only see the PHI relevant to their responsibilities, while multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring multiple verification steps before granting access.
Another essential practice is maintaining audit logs. These logs should track every instance of PHI access or modification. A study published by UCLA in November 2024, available in PMC, highlighted a HIPAA-compliant RPM architecture using platforms like Microsoft Azure and AWS. The system utilized X.509 certificates for secure device authentication, Shared Access Signature (SAS) tokens for verified data uploads, and role-based access control at the database level. To further enhance security, it used NGINX as a reverse proxy, preventing direct user interaction with database components.
Let’s break down the critical steps for protecting PHI and ensuring compliance as your RPM app grows.
Implementing HIPAA-Compliant Security Measures
The HIPAA Security Rule outlines three main categories of safeguards - administrative (policies and procedures), physical (facility access controls), and technical (encryption, access controls, and audit trails). For RPM apps, technical safeguards are especially vital.
Here are some key practices:
- Encrypt PHI in transit and at rest: Use TLS for data in transit and AES-256 for data at rest. While blockchain technology offers end-to-end encryption, it can introduce additional complexity.
- Role-based access control (RBAC): Restrict data access based on user roles. For instance, a cardiologist reviewing heart rate data shouldn't automatically have access to unrelated patient information.
- Two-factor authentication: Make this a standard to enhance login security.
- Audit controls: Keep detailed logs of every access attempt, and use integrity controls to prevent unauthorized changes or deletion of PHI.
When sending notifications, such as push alerts or SMS messages, avoid including sensitive details. Instead of saying, "Your blood pressure reading of 145/92 is elevated", use a message like, "A new health reading is available - please check your app."
Finally, formal agreements with vendors are essential to ensure they also maintain compliance.
Managing Business Associate Agreements (BAAs)
HIPAA compliance isn’t just your responsibility - it extends to every third-party vendor that handles PHI. Vendors like cloud providers, analytics platforms, and outsourced services must sign a Business Associate Agreement (BAA). For instance, AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud offer HIPAA-eligible services and are willing to sign BAAs. Similarly, third-party SDKs such as SendBird and Virgil Security support HIPAA and GDPR compliance, along with certifications like ISO27001 and SOC2 Type 2, ensuring secure telehealth features.
It’s important to regularly review your BAAs, especially when vendors or their services change. If a vendor refuses to sign a BAA, it’s a clear signal to look for alternatives.
Planning for Incident Response and Breach Notifications
Even with strong security measures, breaches can still happen. Under the HIPAA Breach Notification Rule, both covered entities and their business associates are required to notify affected individuals, the HHS Secretary, and in some cases, the media, after a breach of unsecured PHI.
Your incident response plan should include:
- Detection and containment: Define how to identify breaches and limit their impact.
- Notification procedures: Specify who needs to be informed internally and externally.
- Patient communication: Outline how to inform affected individuals clearly and promptly.
Regular security audits and assessments can help identify vulnerabilities before they lead to breaches. Always keep your software updated with the latest security patches. Additionally, user education is critical - train clinicians, patients, and administrators on best practices like creating strong passwords and recognizing phishing attempts.
For added protection, consider data anonymization. Removing identifiable information when full PHI isn’t necessary reduces privacy risks. Comprehensive data governance policies should also be in place, detailing how data is accessed, protected, and managed during breaches. These policies should evolve in response to emerging threats.
With security and compliance under control, the next step is tackling the integration of the diverse IoT devices that power your RPM system.
Integrating IoT Devices and Managing Data Quality
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) apps rely on data from various medical devices - like blood pressure monitors, glucose meters, pulse oximeters, and smartwatches. Each of these devices comes with its own data formats and communication methods, which makes integration a challenge. Building a system that can handle this diversity is crucial. But it’s not just about technical compatibility - you also need to comply with FDA regulations and account for device reliability. Poor integration can lead to incomplete data, missed alerts, and a lack of trust among clinicians. Let’s explore strategies to tackle device integration, data standardization, and protocol compliance.
Integrating Different Medical Devices
There are several ways to integrate medical devices into your RPM system. You could use native device SDKs, partner with third-party aggregators, or create custom gateways. Native SDKs provide direct access to device data but require separate integrations for each manufacturer. On the other hand, third-party aggregators simplify this process by offering a single API for multiple devices.
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) has become the go-to technology for connecting wearables and health trackers. It’s energy-efficient, secure, and works well with devices that handle sensitive health information. To ensure seamless operation, devices often need Wi-Fi or LTE adapters for data transmission. For example, in 2025, OMRON's VitalSight and Philips' HSDP demonstrated how effective integration with EHR systems can reduce the workload for clinicians while ensuring secure data exchange.
When choosing devices, prioritize FDA-cleared options that have been clinically validated for accuracy. Your mobile app should also be compatible with BLE to facilitate smooth data transfer.
Maintaining Data Accuracy and Consistency
As your RPM system grows, it’s essential to normalize incoming data into U.S. customary units and apply validation rules to flag unrealistic readings - like a heart rate over 300 bpm or dangerously low blood pressure levels.
"Collecting accurate patient data with all the specifics of their conditions is essential for successful diagnostics and treatment. Calibrating devices, validating data, and adequately training patients to use monitoring tools can help you achieve this." - Empeek
Patient education plays a crucial role here. Providing clear setup instructions ensures they use the devices correctly, leading to more reliable data. For clinical staff, standardized workflows with clear monitoring protocols and efficient data review processes are equally important.
In 2023, HealthSnap's virtual care platform showcased how seamless EHR integration could eliminate manual data entry, reducing administrative tasks while improving data accuracy. Its analytics engine turned raw data into actionable insights, enabling personalized care plans and better risk management.
Personalized thresholds and alerts tailored to individual patient conditions can help detect and report critical data in real time, enabling timely interventions. AI and machine learning take this a step further by identifying patterns, flagging anomalies, and continuously validating data quality.
Using Standard Communication Protocols
Once you’ve integrated devices and ensured data accuracy, the next step is standardizing communication protocols to maintain interoperability across healthcare systems. This is essential for scaling RPM solutions effectively.
Standards like HL7 and FHIR are widely used to ensure secure API connections with EHR/EMR systems, enabling smooth integration. FHIR, in particular, is favored for its compatibility with modern tech stacks, making it easier to implement and maintain.
Your integration layer should also sync with hospital EMRs and telehealth platforms to streamline workflows for care teams. For instance, the MindMics Health Care project in 2025 demonstrated how real-time data streaming could enable immediate alerting and feedback. Patient data was transmitted to backend systems, where anomalies were automatically flagged for review.
Data typically flows from devices to the mobile app via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi and then to the cloud using cellular or Wi-Fi networks. In some cases, near-field communication (NFC) can be used, provided it balances power consumption, speed, and reliability.
Compliance with regulations is non-negotiable. Beyond HIPAA, you’ll need to consider the HITECH Act, GDPR for international patients, and FDA guidelines for medical device software. Your communication protocols should support end-to-end encryption and define clear data governance policies to ensure secure information flow at every integration point. These measures not only protect patient data but also simplify EHR system integration, making your RPM solution more scalable.
sbb-itb-116e29a
User Experience and Clinical Workflow Integration
Once a secure and scalable infrastructure is in place, the next step in maximizing the potential of an RPM app is creating intuitive user interfaces and clinician tools. These tools must cater to two distinct groups: patients with varying levels of comfort with technology and clinicians who need efficient systems that integrate smoothly into their daily routines. Developing patient-friendly interfaces and streamlined clinical dashboards ensures the RPM app becomes a valuable tool for both groups.
Designing Patient-Friendly App Interfaces
For patients, simplicity is key. A clean and straightforward interface with large touch-friendly areas and prominently displayed essential features can minimize confusion and make navigation easier, whether at home or on the go. Avoid using overly technical jargon; when medical terminology is unavoidable, provide clear definitions to make it accessible.
To accommodate users with disabilities or impairments, consider features like voice commands, adjustable text sizes, high-contrast modes, audio feedback, and compatibility with screen readers. Cross-platform compatibility - spanning smartphones, tablets, and desktops - ensures patients can access their health information in the way that best suits their needs.
Engagement can be further improved with features like basic gamification and customizable settings. For patients with limited digital skills or unreliable internet access, design the app to automatically transmit data when connectivity is available. In the meantime, it should cache data locally to ensure no information is lost.
Optimizing Clinician Dashboards
Clinician dashboards are the nerve center where patient data is reviewed, analyzed, and acted upon. These dashboards need to be intuitive and efficient, keeping in mind the demanding schedules of healthcare providers.
Key features should include tools for rapid risk assessment, alert management, and clear data visualization. For example, dashboards should prioritize patient lists by risk level, offer configurable alerts with tailored thresholds, and include charts or logs to track long-term trends. Secure communication tools - such as one-on-one chats, group messaging, or video conferencing - can facilitate better interactions between clinicians and patients.
Advanced features, like machine learning algorithms, can further enhance the dashboard by analyzing real-time patient data to predict potential health issues. This allows clinicians to intervene proactively, improving outcomes while reducing the need for reactive care.
Integrating RPM Apps with EHR Systems
Seamless integration with Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems is essential for ensuring data continuity and preventing information silos. Using standards like FHIR and HL7 APIs, clinicians can access patient profiles and health data directly from their dashboards, simplifying their workflow.
To make integration effective, establish standardized workflows and clearly defined roles. Training staff regularly and designating "superusers" can help teams adapt to new technology and changes in workflow. Additionally, proactive data management - such as customized alerts synchronized across platforms (email, text, or in-app notifications) - can help reduce alert fatigue and keep clinicians focused on what matters most.
Partnering with Scimus for Scalable RPM Solutions
Creating a scalable Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) application isn’t just about writing code - it’s about balancing technical expertise, healthcare compliance, seamless device integration, and a deep understanding of clinical workflows. Collaborating with a development partner like Scimus, with proven experience in healthcare software, can help you bring your solution to market faster while ensuring it meets strict U.S. regulatory standards. Below, we’ll explore how Scimus delivers quality at every step, from development to deployment.
Healthcare Software Development Expertise
Scimus has a track record of building HIPAA-compliant applications that integrate effortlessly with existing healthcare systems. Their structured six-step development process - Research & Planning, Design & Prototyping, Development, Testing, Launch, and Maintenance - incorporates compliance at every stage. This “compliance-by-design” philosophy ensures regulatory standards are addressed from the very beginning, rather than being tacked on later. This approach is essential for scaling RPM apps while maintaining the highest standards of care.
The Scimus team excels in creating multi-tenant environments and leverages AWS for handling scalable workloads. For example, AWS Lambda enables event-driven processing that adjusts to demand, while AWS CloudWatch continuously monitors system health. Their expertise also extends to integrating with clearinghouses like Availity and EMR/PMS systems such as Experity using API-driven solutions. Security is a top priority, with tools like OneLogin ensuring secure management of sensitive payer portal credentials. A standout example of their work is a 2024–2025 partnership with MedOps, where Scimus developed a scalable solution for real-time insurance eligibility checks. The system launched in under four months, cut manual verification time by more than 90%, and now processes thousands of checks daily across over 50 urgent care practices.
Rigorous Testing and QA for RPM Apps
Reliability is non-negotiable when it comes to RPM apps, as patient safety depends on it. Scimus ensures this through a rigorous quality assurance (QA) process. They conduct unit, integration, and stress testing to catch potential issues before they reach production. Pre-deployment checks are thorough, addressing security vulnerabilities, privacy concerns, and performance bottlenecks. Even after the app goes live, continuous monitoring identifies and resolves bugs or vulnerabilities that could disrupt functionality.
Tailored Engagement Models for Healthcare Needs
Healthcare organizations have diverse needs, ranging from startups to large health systems. Scimus offers flexible engagement options to meet these varying requirements. Whether you need a project-based approach for a specific scope or a dedicated team for ongoing customization, their models adapt to your needs. This flexibility is particularly important for RPM systems, which must accommodate personalized features like custom alert thresholds for patients or workflows tailored to clinical practices.
Scimus takes a user-centered approach, designing solutions that align with local IT infrastructure, clinician workflows, and the socio-economic realities of the healthcare environment. This adaptability ensures their RPM solutions remain scalable and focused on patient-centric care.
Conclusion
Creating a scalable RPM app starts with getting the basics right. The architecture - whether it's modular, microservices-based, or cloud-native - lays the groundwork for a system that can handle increasing demand. At the same time, adhering to HIPAA requirements is a must, with robust encryption, strict access controls, and clear data governance ensuring patient data stays secure. Reliable IoT integration and accurate data collection are equally important to keep patient information both trustworthy and actionable.
Technical performance is only half the equation; user experience plays a key role too. Patients need interfaces that are simple and easy to navigate, while clinicians depend on smooth, efficient dashboards that work seamlessly with EHR systems. When these elements come together, an RPM solution doesn’t just work - it scales effectively, improves patient outcomes, and helps reduce costs.
The potential for growth in this space is undeniable. For instance, the global RPM market is expected to hit $190.8 billion by 2030. In the U.S., over 80% of people support remote patient monitoring. By focusing on well-designed, compliant, and user-friendly RPM apps, healthcare providers can not only meet rising demand but also deliver measurable improvements in care. Collaborating with experienced development teams can further speed up the journey to market.
Building with scalability in mind sets the stage for better care, greater efficiency, and sustainable growth. By prioritizing architecture, compliance, IoT integration, and user experience from the start, you can create RPM apps that grow alongside your organization's goals. This approach turns RPM into a powerful tool for enhancing both patient care and operational efficiency.
FAQs
What are the benefits of using a microservices architecture for scaling remote patient monitoring apps?
A microservices architecture helps remote patient monitoring (RPM) apps grow and adapt by dividing the application into smaller, self-contained services. Each service operates independently, meaning it can be deployed, managed, and scaled on its own. This flexibility ensures resources are used efficiently and the app can handle increasing numbers of users without running into performance issues.
This setup also boosts the system's reliability. If one service runs into a problem, it doesn’t bring the entire app down. On top of that, microservices make it simpler to roll out updates or introduce new features, keeping the app aligned with the ever-changing needs of healthcare.
What are the essential security measures for ensuring HIPAA compliance in remote patient monitoring apps?
To make remote patient monitoring (RPM) apps align with HIPAA requirements, several steps are essential. Start with secure data encryption - this ensures that sensitive information is protected both while being transmitted and when stored. Implement strict access controls to restrict who can access patient data, and add an extra layer of security with multi-factor authentication for user accounts.
Regular security audits are a must to uncover potential weak spots, and staff training plays a key role in maintaining a strong security posture. Lastly, make sure your app is developed on a HIPAA-compliant platform and adheres to established protocols for protecting patient information. These measures collectively help safeguard sensitive data and maintain compliance.
How do remote patient monitoring (RPM) apps connect with IoT devices while ensuring data accuracy and compliance?
RPM apps work hand-in-hand with IoT devices like wearable sensors and health trackers, using Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) or Wi-Fi to enable smooth and secure data sharing. These apps are designed with healthcare regulations in mind, such as HIPAA, ensuring data encryption and seamless integration with electronic health record (EHR) systems.
To maintain data accuracy, RPM solutions depend on FDA-cleared devices, real-time monitoring, and backup systems that temporarily store data during connectivity issues. They also follow industry standards like HL7 to ensure compatibility and dependability. Customizable alerts and workflows further enhance clinical safety while meeting necessary regulatory requirements.

