Automated web scraping transforms how SaaS platforms collect and use data. Instead of relying on slow, error-prone manual methods, SaaS companies use automated tools to extract data from websites quickly and accurately. This data fuels critical tasks like price monitoring, market research, and personalized user experiences.
Key Takeaways:
- What it is: Automated web scraping uses tools to extract and structure data from websites.
- Why it matters: SaaS platforms depend on real-time data for competitive analysis, market trends, and user personalization.
- Benefits:
- Speed: Processes data in minutes instead of weeks.
- Scalability: Handles millions of pages with minimal effort.
- Accuracy: Reduces human errors with consistent rules.
- Market Growth: The web scraping software market is projected to grow from $1.01 billion (2024) to $2.49 billion by 2032.
By automating data collection, SaaS platforms can stay competitive, make quick decisions, and deliver better services - all while navigating technical and legal challenges.
Web Scraping 101: A Million Dollar SaaS Idea
Benefits of Automated Web Scraping for SaaS Platforms
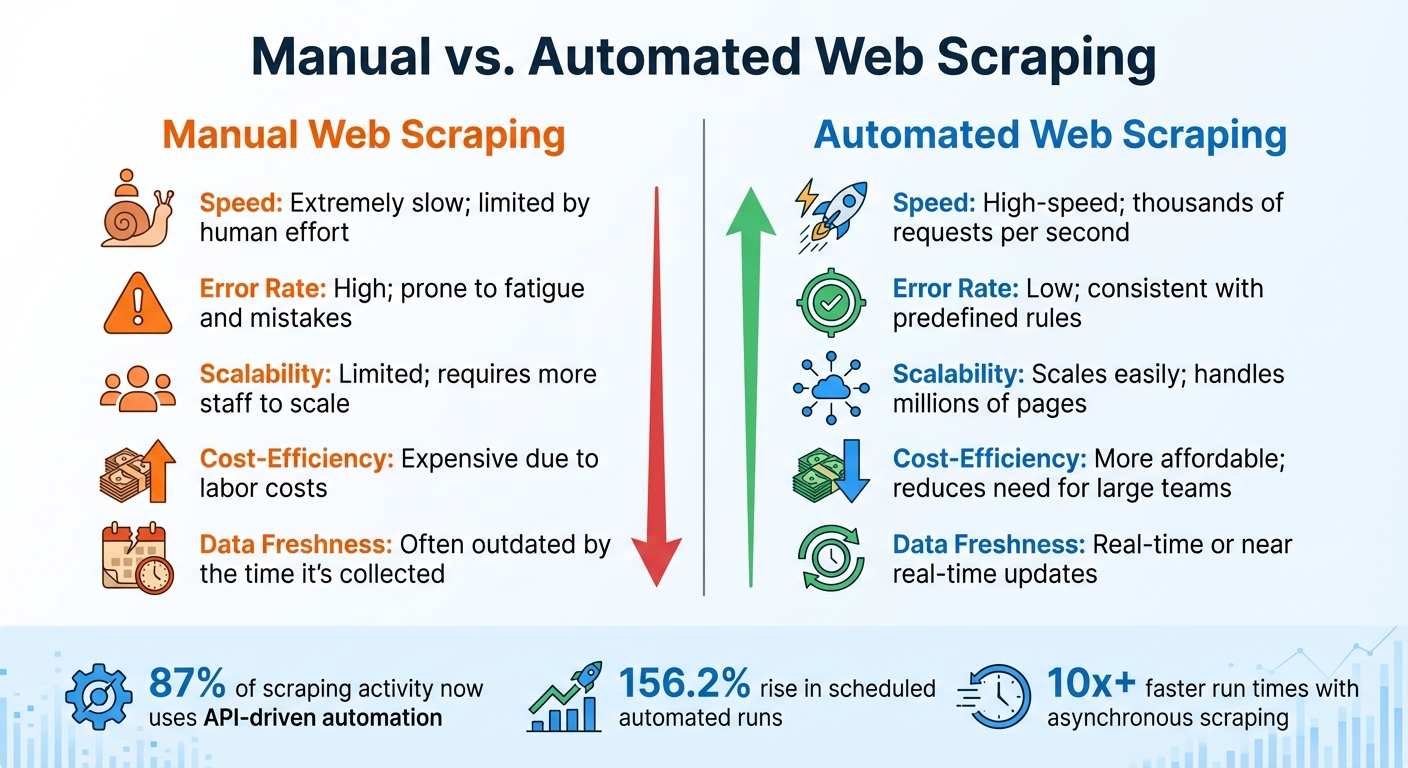
Manual vs Automated Web Scraping: Speed, Accuracy, and Scalability Comparison
Automated web scraping offers three key advantages that manual data collection can't compete with: speed, scalability, and accuracy. These benefits allow SaaS platforms to stay agile, make quick decisions, and rely on up-to-date, reliable data - giving them a strong edge in competitive markets.
Speed and Efficiency
Automated scrapers can process thousands of requests simultaneously, while manual methods are stuck handling one page at a time. Tools like asyncio and httpx enable asynchronous scraping, cutting run times by more than 10x compared to traditional, synchronous methods.
"Speed is by far the biggest benefit of automated web scraping because it handles monotonous tasks without fatigue, limited only by technical constraints." - Kevin Sahin, Co-founder of ScrapingBee
Automation also eliminates the need for hours of manual reformatting by instantly converting unstructured data into structured formats like JSON or CSV. For SaaS platforms that depend on real-time data - like pricing updates - this speed is critical. Automated tools use APIs to manage proxy rotation and user-agent configurations, ensuring data pipelines remain functional even when faced with IP blocks. These efficiency gains make it possible for SaaS platforms to handle large-scale, accurate data processing with ease.
Scalability and Accuracy
When it comes to scaling, automation is in a league of its own. Manual processes grow linearly with data demands - doubling your data needs means doubling your workforce. In contrast, automated systems can process millions of pages with minimal additional resources.
Accuracy also benefits from automation. Automated pipelines use validation schemas to maintain data integrity. Unlike humans, who are prone to errors like copy-paste mishaps, scrapers follow predefined rules with absolute consistency. Advanced AI-powered scrapers take this a step further by identifying key data points - like prices or product names - even when website structures change. This adaptability reduces maintenance efforts and keeps data pipelines running smoothly.
Manual vs. Automated Web Scraping
Here’s how manual and automated scraping stack up:
| Feature | Manual Web Scraping | Automated Web Scraping |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Extremely slow; limited by human effort | High-speed; thousands of requests per second |
| Error Rate | High; prone to fatigue and mistakes | Low; consistent with predefined rules |
| Scalability | Limited; requires more staff to scale | Scales easily; handles millions of pages |
| Cost-Efficiency | Expensive due to labor costs | More affordable; reduces need for large teams |
| Data Freshness | Often outdated by the time it's collected | Real-time or near real-time updates |
The numbers tell the story: API-driven automated scraping now accounts for 87% of all scraping activity on major platforms, with a 156.2% rise in scheduled automated runs. This shift toward "always-on" data collection highlights why automation is becoming essential for SaaS platforms that rely on real-time insights.
How SaaS Platforms Use Web Scraping
Web scraping has become a cornerstone for tasks like competitive analysis, market research, and creating personalized user experiences. It takes raw data from various sources and turns it into actionable insights that drive strategy and improve customer satisfaction. In fact, 73% of companies now rely on web scraping for market insights and competitor tracking, showing just how integral this tool has become.
Competitive Analysis and Price Monitoring
One of the most impactful uses of web scraping is in competitive analysis, particularly for monitoring prices, stock levels, and promotions in real time. By leveraging automated scraping, companies can implement dynamic pricing strategies, which have been shown to increase revenue by 2–5% and improve profit margins by up to 10%.
Modern scraping tools go beyond basic data collection. They employ advanced technologies like headless browsers and AI to navigate obstacles such as CAPTCHAs and JavaScript-heavy websites. These innovations ensure a steady flow of data, even as websites continuously upgrade their defenses.
"Knowledge is power. And web scraping takes all of these actions in a shorter time, more affordable, and more convenient way." - Mert Bekci, Lead Software Engineer, Scrape.do
But competitive analysis is only one piece of the puzzle. Web scraping also plays a major role in broader market research.
Market Research and Lead Generation
Web scraping has replaced many traditional research methods, such as surveys, by offering real-time data collection. SaaS platforms use it to automate the gathering of contact details like emails, phone numbers, and other firmographic data from business directories, social media, and professional networks. The result? Highly targeted and segmented prospect lists.
Beyond generating leads, scraping enables companies to track consumer sentiment and spot market trends in real time. By analyzing data from social media, blogs, and news outlets, SaaS platforms can identify opportunities and emerging trends faster than their competitors. With the global web scraping software market expected to hit $2.49 billion by 2032, it’s clear that demand for these capabilities is only growing.
This wealth of data doesn’t just inform strategy - it also enhances the user experience.
Personalized User Experiences
Using web scraping to analyze reviews and industry content allows SaaS platforms to perform sentiment analysis and deliver tailored user experiences. For example, by automatically pulling in the latest articles and insights, these platforms can create personalized feeds that match individual user preferences. This transforms what could be a generic interface into a dynamic, customized environment that adapts to each user’s needs.
Tools and Technologies for Automated Web Scraping
Choosing the right tools and techniques is essential for achieving the speed, scalability, and precision needed in modern SaaS data solutions. The choice of tools often depends on the type of data - static or JavaScript-rendered - and the scale of operations.
Common Scraping Tools and Frameworks
BeautifulSoup is a Python library designed for parsing static HTML. While it's efficient for simpler tasks, it doesn't support JavaScript-rendered content.
Scrapy stands out as an asynchronous framework for large-scale scraping. It includes features like a request engine, spiders for implementing extraction logic, and item pipelines to export data into databases like MongoDB or PostgreSQL. With over 700 plugins available on GitHub, Scrapy's functionality can be extended to include proxy rotation, caching, and more.
For dealing with dynamic websites and single-page applications, tools like Puppeteer and Playwright are invaluable. These headless browsers can handle complex tasks such as rendering infinite scrolls or processing AJAX calls. Playwright, in particular, supports multiple browsers - including Chromium, Firefox, and WebKit - making it a versatile option for cross-browser scraping.
Many scraping tools also offer REST or GraphQL APIs, which return structured data formats like JSON or XML. These APIs simplify integration with data pipelines for SaaS platforms. Managed platforms like Browserless go a step further, providing out-of-the-box infrastructure that includes proxy rotation and CAPTCHA solving via a single API endpoint.
These tools form the backbone of web scraping, but overcoming modern anti-scraping measures requires more advanced techniques.
Advanced Scraping Techniques
Navigating anti-scraping defenses often calls for a mix of technical strategies. Proxy rotation is one of the most effective methods to avoid IP bans. Residential proxies are particularly effective because they mimic real home or mobile users, making them harder to detect compared to datacenter proxies. Another useful tactic is randomizing User-Agent strings to simulate different browsers. For handling CAPTCHAs, services like 2Captcha can solve challenges at a per-thousand rate, ensuring uninterrupted data collection.
Another method is sniffing AJAX endpoints, which allows you to bypass heavy JavaScript rendering and access cleaner, structured data. This approach reduces the risk of disruptions caused by changes to a website's visual layout.
A benchmark conducted in 2025 compared 13 scraping engines across 1,000 real-world URLs. Results showed that Firecrawl achieved an 80.9% success rate, significantly outperforming standard Playwright implementations, which managed only 39.5% due to anti-bot challenges.
"A web scraper turns the web into data you can actually work with." – Alejandro Loyola, Technical Support, Browserless
Before diving into scraping, always check if the target site offers an official API. APIs are typically more reliable, ethical, and efficient than scraping raw HTML. For high-volume scraping, implement retry mechanisms to handle server errors like HTTP 503 and introduce random delays between requests to avoid being flagged as a potential DDoS attack.
These advanced strategies not only help you navigate anti-scraping measures but also ensure the reliability and efficiency of data pipelines critical for modern SaaS platforms.
sbb-itb-116e29a
How Scimus Builds Web Scraping Solutions for SaaS Platforms

Custom Development for Scalable Data Pipelines
Scimus begins each project by clearly defining the data requirements, KPIs, and data lineage to ensure alignment with the specific goals of the SaaS platform. The choice of tools depends on the complexity of the target websites: BeautifulSoup is typically used for static pages, while Selenium or Playwright come into play for JavaScript-heavy sites. To tackle anti-scraping measures like CAPTCHAs, browser fingerprinting, and firewalls, Scimus integrates tailored solutions into every project.
By using modular script architectures, Scimus separates the logic for HTML interaction from processes like data cleaning and storage. This thoughtful design not only simplifies updates when website structures change but also reduces maintenance costs and time. Additionally, proxy rotation and rate limiting are customized for each project’s needs, ensuring efficient and reliable data collection. These tailored approaches lay a solid foundation for thorough quality assurance, guaranteeing consistent performance.
QA and Automation Testing for Reliable Performance
Once development is complete, Scimus prioritizes rigorous quality assurance to maintain data accuracy and reliability. Automated monitoring systems are put in place to detect any changes in HTML, CSS selectors, or XPaths, enabling developers to address potential script issues before they disrupt operations. QA processes include multi-layered data validation and robust error-handling mechanisms, such as exponential backoff to manage network or server errors effectively.
Key performance metrics - like pages scraped per hour, request success rates, extraction times, and data volume - are continuously tracked. Tools like the ELK stack are used for centralized logging, capturing errors and triggering real-time alerts when issues arise.
"Manual scraping is way too slow, error-prone, and not scalable." – Kevin Sahin, Co-founder, ScrapingBee
To ensure the data is ready for business-critical decisions, Scimus sanitizes and normalizes the scraped output. This involves removing duplicates, standardizing text casing, and aligning date and time formats. With this thorough QA process, SaaS platforms can rely on clean, dependable data to drive their operations forward.
Challenges and Ethics in Web Scraping
Anti-Scraping Measures and Technical Obstacles
Websites employ a range of tactics to block scrapers, including IP blocking, CAPTCHAs, and honeypot traps, which are designed to identify and deter automated tools. Advanced systems now go even further, analyzing details like TLS fingerprints, HTTP headers, and user behavior - such as mouse movements and scrolling speeds - to distinguish bots from human users. On top of that, platforms increasingly rely on AI-powered Web Application Firewalls from companies like Cloudflare and Akamai to detect and respond to scraping activities in real time. Additional challenges include dynamic content rendered through JavaScript, infinite scrolling interfaces, and login walls, all of which complicate the data extraction process.
"Large-scale scraping isn't about writing better code, it's about building a system that can survive the chaos." – Mert Bekci, Lead Software Engineer, Scrape.do
To navigate these defenses, scrapers often rotate IP addresses, change User-Agent strings, and introduce random delays to reduce server strain and avoid detection. They are also programmed to bypass traps by ignoring HTML elements with properties like display: none or visibility: hidden. For errors like HTTP 503, retry mechanisms with exponential backoff are employed to ensure the scraper can recover and continue operating. These strategies are critical for SaaS platforms aiming to maintain accurate and reliable data pipelines.
Legal Compliance and Ethical Practices
Technical expertise alone isn’t enough - scraping must also adhere to legal and ethical standards. A good starting point is respecting a website's robots.txt file and ensuring compliance with regulations like GDPR, which governs personal data protection in Europe. For instance, in January 2023, the French regulator CNIL fined KASPR €240,000 for scraping LinkedIn data without obtaining user consent.
To avoid legal complications, platforms should space requests 1–2 seconds apart, reducing server load and minimizing the risk of claims under doctrines like "Trespass to Chattels". Transparency is another key factor - using a clear User-Agent string that identifies the bot and provides contact details demonstrates good faith. Ethical practices also include data minimization, which involves collecting only essential information and filtering out personally identifiable data (PII) to comply with GDPR and CCPA guidelines.
The consequences of non-compliance can be severe. GDPR violations can result in fines of up to €20 million or 4% of a company’s global revenue, while copyright violations in the U.S. may lead to damages as high as $150,000 per work if data is used without permission. Ethical scraping also involves avoiding peak business hours to reduce server strain, maintaining detailed audit logs of scraping activities, and obtaining consent before republishing any data to respect intellectual property rights.
Conclusion
Automated web scraping has become a cornerstone for modern SaaS platforms, turning unstructured web data into actionable insights that fuel competitive growth. The market for web scraping software, valued at $1.01 billion in 2024, is projected to soar to $2.49 billion by 2032. Meanwhile, the alternative data market - worth $4.9 billion in 2023 - is expected to grow at an impressive rate of 28% annually through 2032. Companies use scraping tools for tasks like real-time price tracking, lead generation, and creating tailored user experiences. For instance, retailers leveraging optimized pricing strategies have seen sales increase by about 4%.
The shift toward automation is clear: 87% of scraping now happens via API-based automated processes instead of manual efforts. Additionally, AI-powered "self-healing" scrapers are replacing older, rule-based systems that were prone to breaking. As SO Development aptly puts it:
"The future of scraping is not code - it's intent."
However, successful web scraping requires a careful balance between technical execution and ethical practices. While only 17.4% of developers see scraping as "legal and unrestricted", 68% cite blocking as their biggest challenge. To avoid issues, platforms must respect robots.txt files, use throttling to prevent server overload, and comply with regulations like GDPR and CCPA to steer clear of significant penalties.
Scimus supports businesses in navigating these hurdles by building custom, scalable data pipelines. Their approach emphasizes rigorous QA and automation testing, ensuring reliable performance, precise data, and adherence to legal standards. This helps SaaS platforms harness the full potential of web data extraction while staying compliant and secure.
FAQs
How do SaaS platforms stay compliant with legal and ethical web scraping standards?
SaaS platforms take care to stay within legal and ethical boundaries when it comes to web scraping. They closely examine laws such as copyright regulations, the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA), and data privacy rules like GDPR or state-specific protections. Before gathering any data, they establish a solid legal basis - often leaning on legitimate interest or obtaining explicit consent, especially when personal information is involved. Additionally, they honor site-specific guidelines, like robots.txt files and rate limits, and avoid breaching terms of service or copyright laws.
On the ethical side, these platforms adopt measures to ensure responsible data handling. For example, they store only the data that’s absolutely necessary, safeguard it with encryption, and routinely review retention policies. They adhere to data minimization principles, exclude personal data unless consent is given, and keep a clear record of the purpose and source of the information they collect. By combining legal diligence, privacy-focused engineering, and a commitment to transparency, SaaS platforms can responsibly leverage web scraping while meeting both legal and ethical standards.
What techniques are used to bypass anti-scraping defenses?
To work around anti-scraping defenses, developers rely on advanced techniques that mimic real user behavior. One popular tactic involves using full-browser automation tools like Selenium or Playwright, which can handle JavaScript-rendered pages in the same way a human browser would. For simpler setups, combining frameworks like Scrapy with JavaScript rendering tools such as Splash is a common choice for managing dynamic content.
Another key strategy is avoiding detection by rotating residential proxies or IP pools, enabling scrapers to appear as though requests are coming from different locations. Additionally, "stealth" browser settings are used to disguise automation, while user agents, headers, cookies, and request timing are randomized to further blend in. To replicate human activity, techniques such as scrolling, mouse movements, and even CAPTCHA-solving services are integrated. These combined efforts allow SaaS platforms to extract data effectively while keeping pace with ever-evolving anti-scraping technologies.
How does automated web scraping create more personalized experiences for SaaS users?
Automated web scraping plays a key role in collecting fresh public data, which powers AI and analytics within SaaS platforms. This data drives features such as real-time personalized recommendations, dynamic pricing adjustments, and content that aligns with user sentiment, all finely tuned to match individual preferences and behaviors.
By handling vast amounts of data continuously, SaaS platforms also enable AI-driven chatbots to provide smart, responsive interactions that adapt to user needs. This not only enhances user engagement but also helps businesses deliver tailored experiences, keeping them ahead in a competitive market.

